Understanding how the ACT is scored is essential if you want to interpret your results properly – and use them strategically in your US university applications.
Although the ACT looks straightforward on the surface, the scoring system involves several layers: raw scores, scaled scores, composite scores, optional section scores, and additional scores for STEM and English Language Arts.
In this guide, we explain:
- How raw and scaled scores work
- How your Composite Score is calculated
- How the Writing section is marked
- What STEM and ELA scores mean
- What counts as a good ACT score
- What competitive universities, including the Ivy League, typically expect
By the end, you will have a clear understanding of how the ACT scoring system works – and what your scores actually mean in context.
Note: this guide is updated to reflect the changes to the ACT format announced in 2025.
How is the ACT Scored?
Before we explain how the ACT is scored, a brief overview of the sections in the test will be useful. The ACT consists of five different sections:
- English, Reading, and Math are the compulsory sections. These are all multiple-choice with a single correct answer to each section.
- Science is optional. It is also multiple-choice.
- Writing is optional. It consists of a single essay.
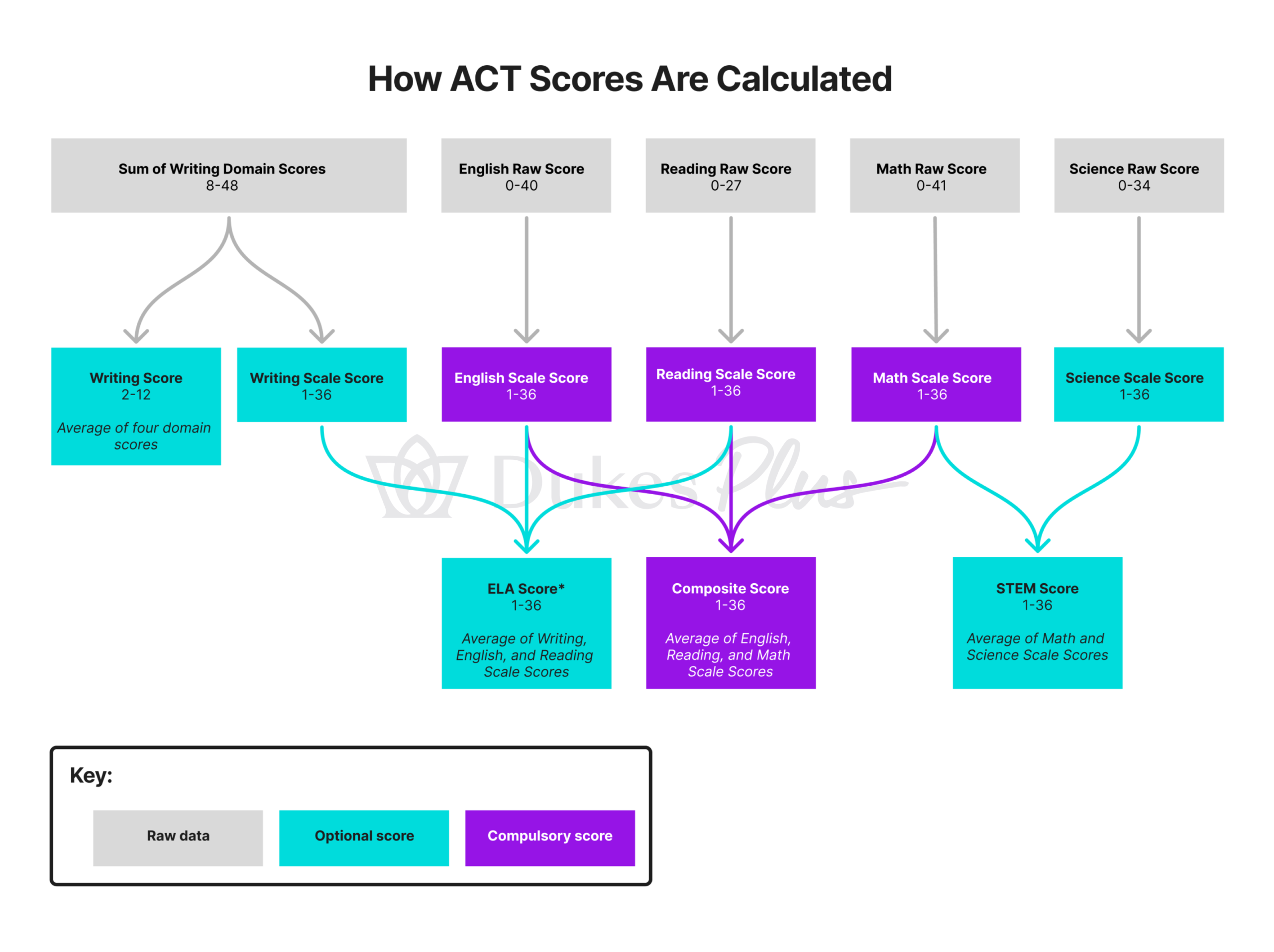
English, Reading, Math, and Science
Raw Scores
In the English, Reading, Math, and Science sections, you first receive a ‘raw score’ – this is simply the number of questions you answer correctly. You don’t lose any marks for incorrect answers.
However, there is a minor caveat to this: only ‘operational’ questions count towards your raw score. What’s an operational question? In each section of the ACT, they include a small number of ‘field test’ questions – these are questions which they are trying out for potential future tests. Your answer to these questions doesn’t count towards your raw score for that section. It’s only the operational questions – i.e. the ones which aren’t field tests – which count.
Each section has a different number of operational questions:
| Section | Total questions | Operational questions | Field test questions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Math | 45 | 41 | 4 |
| English | 50 | 40 | 10 |
| Reading | 36 | 27 | 9 |
| Science | 40 | 34 | 6 |
So for instance, your maximum raw score for the ACT Math section is 41; English is 40, etc. You could get all the field test questions right or all of them wrong and it wouldn’t affect your raw score.
Unfortunately there is no way to distinguish between operational and field test questions when taking the test – you have to do your best to get every question right.
Scaled Scores
For each of these four sections, the ACT then scale your raw score to a scaled score between 1 and 36 (where 36 is the best).
The scaling process is designed to account for differences in difficulty between different test sittings. If students got lower raw scores on average in one section in a certain sitting of the ACT, then this would be deemed a harder sitting. The students in this sitting would then see their scaled score bumped up slightly compared to students who had got the same score for that section in an easier sitting.
To illustrate with some purely theoretical (and simplified) numbers for the Math section:
| Section | Average raw score | Example raw score | Example scaled score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sitting 1 | 25 | 32 | 25 |
| Sitting 2 | 23 | 32 | 27 |
Composite Score
The ACT Composite Score is calculated as the average of your three scaled scores for the three compulsory sections (English, Reading, and Math). Averages are then rounded to the nearest whole number.
Like the section scaled scores, the Composite Score is therefore also out of 36.
For instance, let’s say your scaled scores were:
- English – 22
- Math – 24
- Reading – 20
Then your Composite Score would be: (22 + 24 + 20) / 3 = 22
Your scores for the Science and Writing sections, should you choose to take them, do not count towards your Composite Score.
Improve Your ACT Score
Boost your ACT score by 7+ points with our programmes of elite preparation, delivered by Ivy League graduates and expert tutors.
Writing Score
The Writing section is scored differently from the other, multiple-choice sections.
Two raters will grade your essay on four different ‘domains’:
- Ideas and Analysis
- Development and Support
- Organization
- Language Use and Conventions
You will get a score on a scale of 1-6 (where 6 is best) from each rater for each domain, meaning your total score for each domain will be between 2 and 12, and for the section as a whole, between 8 and 48.
Two things then happen to your total between 8 and 48:
- It is scaled to between 1 and 36, in the same way as the other sections, to give your ACT Writing Scaled Score
- It is divided by four to give your ACT Writing Score, which is between 2 and 12
Your total between 8 and 48 is then scaled.
Your Writing Score does not affect your ACT Composite Score. However, it does feed into your ELA Score – more on that in the next section.
STEM and ELA Scores
As well as your scores for each section and your Composite Score, the ACT also provides two more scores:
- STEM score
- ELA (English Language Arts) score
The STEM score is the average of your Math and Science scaled scores. You need to take the optional Science section to get a STEM score.
The ELA score is the average of your English, Reading, and Writing scaled scores. You need to take the optional Writing section to get an ELA score.
Example
Let’s say a student took all five sections of the ACT, including optional Writing and Science sections. Their scaled scores were:
- English – 25
- Math – 29
- Reading – 27
- Writing – 24
- Science – 31
Their Composite Score would be calculated as: (25 + 29 + 27) / 3 = 27
Their STEM score would be: (29 + 31) / 2 = 30
Their ELA score would be: (25 + 27 + 24) = 25.33 –> rounded to nearest whole number = 25
When did the ACT Change from 32 to 36?
If you remember that the ACT was once scored out of 32, you either have a long memory or a keen interest in the history of standardised testing.
The ACT changed from being out of 32 to 36 when it rebranded as the Enhanced ACT in 1989. Various other changes to the test took place at this point, too:
- The Social Studies section was replaced by Reading
- The Natural Sciences section was replaced by Science Reasoning
When do ACT scores come out?
ACT scores are usually released within two weeks of your test date, unless you took the Writing section.
If you took the Writing section, then your scores will be released 5-8 weeks after your test date. Your scores for the other sections will most likely be ready within 2 weeks but the Writing section takes longer to mark, and your scores will be reported only after all your section scores are available.
What is a Good ACT Score?
The table below shows how all ACT test-takers perform in each section and with their Composite Score:
| Percentile | Composite | English | Math | Reading | Science | Writing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100th | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 12 |
| 90th | 28 | 28 | 27 | 31 | 27 | 8 |
| 75th | 23 | 23 | 23 | 24 | 23 | 7 |
| 50th | 18 | 18 | 17 | 19 | 19 | 6 |
| 25th | 14 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 15 | 5 |
| Mean | 19.2 | 18.6 | 19 | 20.1 | 19.6 | 6.1 |
A Composite Score of 18 or above would place you in the top half of all test-takers, while 23 would place you in the top 25%, and 28 in the top 10%.
However, a good ACT score for each student depends on which universities you are aiming for. Selective colleges will expect scores in the high 20s and the most competitive, such as the Ivy League, will expect scores in the 30s. Many applicants for these colleges will get Composite Scores of 33+.
Good Score for Writing
As we discussed earlier, the Writing section is scored differently. Your Writing score is on a scale of 2-12.
A score of 8 will place you in the top 10% of test-takers and a score of 7 in the top 25%.
Average ACT Score
The average ACT score is 19.2.
Perfect ACT Score
A perfect ACT Composite Score is 36 out of 36 – although in theory, you could achieve this by getting 36 in two of the compulsory sections and 35 in the third. A truly perfect score might involve getting 36 in all three compulsory sections – or even in all five sections, including the optional Science and Writing sections.
What is a Good ACT Score for the Ivy League?
A good ACT Score for the Ivy League is 35+.
The table below shows the ACT Composite Scores for accepted applicants at each Ivy League school:
| University | 25th percentile | Median | 75th percentile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brown | 34 | 35 | 35 |
| Columbia | 34 | 35 | 35 |
| Cornell | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| Dartmouth | 32 | 33 | 35 |
| Harvard | 34 | 35 | 36 |
| Penn | 34 | 35 | 35 |
| Princeton | 34 | 35 | 35 |
| Yale | 33 | 34 | 35 |
A good score for the Ivy League would be one that places you in the 75th percentile or above of accepted applicants. This is the point at which your score would begin to definitely advantage your application.
We can see that for most colleges, this score is 35. At Harvard, it is a perfect 36.
ACT Preparation from Dukes Plus
Want to get the highest ACT score possible?
At Dukes Plus, our expert ACT preparation has helped students improve their scores for more than 20 years. Our ACT prep course offers an intensive guide to the content and key test strategies to excel, while our ACT test tutoring helps students increase their score by 7 points on average.
Book a free consultation to learn more.
Speak to an Expert
Applying to US universities?
Book a free call with a member of our expert team to discover how we can support your application.
FAQs
ACT scores are usually released within two weeks of your test date.
If you took the Writing section, your scores are typically released 5–8 weeks after your test date. Although your multiple-choice section scores may be ready earlier, all results are released together once the Writing section has been marked.
For Harvard University, a competitive ACT Composite Score is:
- 34 – 25th percentile of accepted students
- 35 – Median score
- 36 – 75th percentile
A good ACT score for Harvard is therefore 35 or above. A 36 places you in the strongest statistical position.
The ACT scoring process works in several stages.
First, you receive a raw score in English, Math, Reading, and Science. You earn one point for each correct answer and there is no penalty for incorrect answers.
Maximum raw scores are:
- Math – 41
- English – 40
- Reading – 27
- Science – 34
Next, your raw score in each section is converted into a scaled score between 1 and 36. The scaling process adjusts for differences in difficulty between test sittings.
Your Composite Score is the average of your scaled scores in English, Math, and Reading. This average is rounded to the nearest whole number. Science and Writing do not count towards the Composite Score.
If you take the Writing section, it is scored separately. You receive:
- A scaled Writing score between 1 and 36
- A separate Writing score between 2 and 12
The Writing score does not affect your Composite Score.
The ACT also provides:
- A STEM score, which is the average of Math and Science
- An ELA score, which is the average of English, Reading, and Writing
The ACT Writing score is on a scale of 2 to 12.
- A score of 8 places you in the top 10% of test-takers.
- A score of 7 places you in the top 25%.
A score of 8 or above is considered strong, particularly for competitive universities.
A good ACT score for the Ivy League is 35 or above.
For most Ivy League universities:
- 33–34 is around the lower end of the accepted range.
- 35 is at or above the 75th percentile for many schools.
- 36 is the strongest possible score.
To be clearly competitive, you should aim for 35+.
The ACT changed from being scored out of 32 to 36 in 1989, when it rebranded as the Enhanced ACT.

